Shipping Perks
Money Back Guarantee

Customer Service

Nontoxic Printmaking
Introduction to Drone Frequency Bands
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), utilize various frequency bands for communication, control, and data transmission. Understanding these frequency bands is essential for ensuring safe and effective operation. Below are some commonly used frequency bands in drone technology, including GPS frequencies. 1. 2.4 GHz ISM Band 2. 5.8 GHz ISM Band 3. 900 MHz ISM…
What Should I Consider When Purchasing a Drone Jammer?
As drones become more prevalent in various sectors, the demand for drone jammers has increased significantly. Whether you’re looking to enhance security at an event, protect sensitive locations, or simply prevent unauthorized drone usage, it’s essential to choose the right jammer. Here are some key factors to consider when purchasing a drone jammer. 1. Output Power…
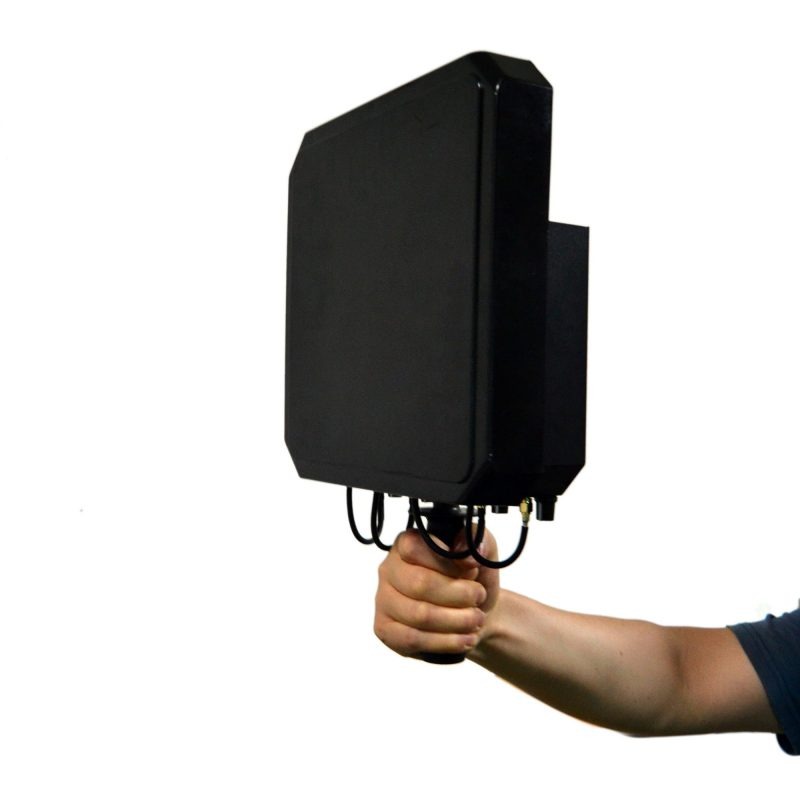
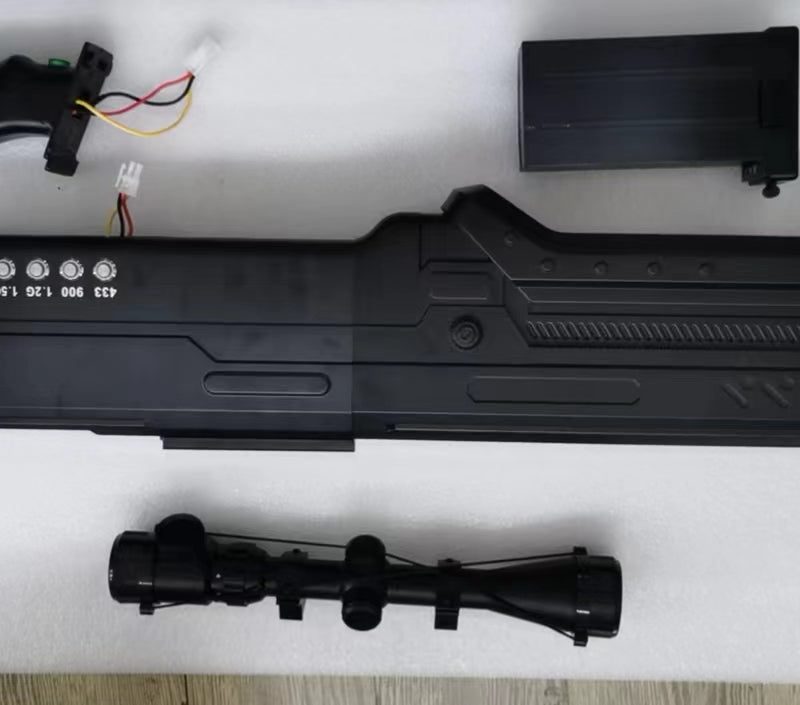
Desktop or Portable Drone Jammer?
When considering the type of jammer to use, one of the most important factors to keep in mind is whether you need a desktop jammer or a portable jammer. Desktop Jammers Desktop jammers typically offer higher output power, allowing them to cover larger areas effectively. This makes them particularly suitable for use in spacious environments…
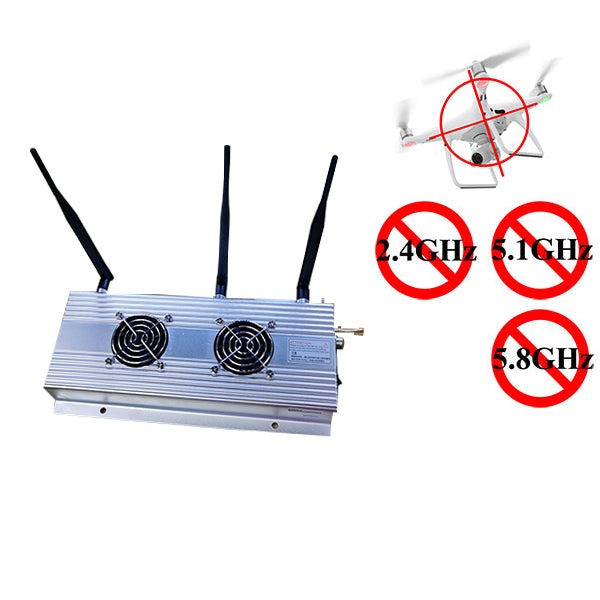
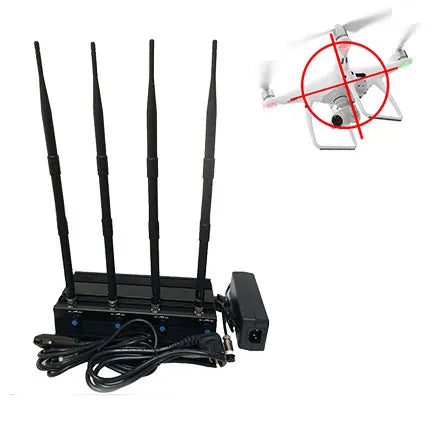
What Frequency Band Do Drone Jammers Interfere With?
Drone jammers primarily operate within specific frequency bands to disrupt the communication between drones and their operators. The key frequency bands targeted by these jammers include: Applications of Drone Jammers Drone jammers are mainly applicable in high-security locations and critical facilities where safety and privacy are paramount. Some of the key areas where these devices…
Where is the Drone Detection and Countermeasure Equipment Installed?
In recent years, the proliferation of drones has raised significant security concerns, particularly in sensitive and high-stakes environments. To address these challenges, various institutions have begun to deploy drone detection and countermeasure equipment in strategic locations. This article explores the key areas where such equipment is typically installed. 1. Government and Military Facilities One of…
Do Drone Jammers Work?
Drone frequency jammers are devices designed to disrupt the communication signals between a drone and its operator. They function by emitting stronger signals on the same frequencies that the drone relies on for communication. This process effectively drowns out the legitimate signals, making it difficult or impossible for the drone to receive commands from its…
FPV Drone Has Become a Combat Tool in Modern Warfare
As we all know, FPV drone is a high-speed development product, and nowadays, due to the widespread use of FPV drones, it has become a common tool of war. Why FPV system can be a very important device in war, one of the reasons is because , that it can match with multiple sensors and…
Why Choose Us ?
Thank you for choosing uavJammer123. We deeply appreciate your trust, and we will do our utmost to provide you with the highest quality products and services.
What Is A Drone Signal Jammer?
UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) jammers are devices that operate at the same frequency as quadcopters and jam data transmission. However, the matter is not limited to this; they can completely disable the control of the flying device, causing it to either land on the ground or be carried away by the wind in an unknown…









